From Data to Insights
In today’s dynamic business environment, data, despite all its benefits, is often seen as complex and burdensome. If you’re responsible for strategic decision-making and company growth, you’ve likely been under pressure to make your data usable and future-proof, and you also know the frustration that follows this.
While AI and ML technologies make it seem effortless for organizations to achieve synergies from Day 1, to work as well as they promise, they require a continuous flow of clean, structured, real-time data—which can only be provided with a solid data foundation.
The perception of data as a liability
As organizations rely more and more on technology for their operations, they inevitably accumulate vast amounts of data, including customer information, financial records, and operational data. However, this abundance is not always cause for celebration: Veritas states that on average, enterprises store 10 PB of data, and only 15% of this data is considered business critical, while a whopping 85% of this data is Dark or ROT (Redundant, Obsolete or Trivial) data.
Imagine being a Business Analyst, eager to dive into customer data and uncover valuable insights; however, the reality is far from the hype: instead of clear answers, you're drowning in a sea of information scattered across different systems. Much of it is old, irrelevant, or missing key details. It's like trying to find a needle in a haystack while deadlines loom ahead.
The truth is, while everyone talks about the power of data, they often overlook the real challenges:
- Data overload: Companies collect so much data it becomes overwhelming and hard to manage.
- Privacy and compliance: Strict rules about protecting customer data create extra work, as Meta found out in 2021, when they were fined €1.2 billion ($1.3 billion) for violating laws in data transfer between the EU and the USA, making it one of the biggest GDPR fines yet.
- Security Risks: Keeping data safe is expensive and breaches can be catastrophic. Companies from Facebook and X (Twitter) to JP Morgan Chase and the US Military have experienced disastrous data breaches over the years.
- Lack of insights: Companies struggle to make sense of their data to get useful information.
- Data waste: A lot of data is useless or duplicated, and the important stuff is often missing.
In short, data can be a double-edged sword. While it offers potential for great insights, getting there is often messy and frustrating. Without proper oversight and management, data becomes a dumping ground rather than a gold mine.
Shifting the Perspective: Exploring Opportunities with Data
Data is no longer just a by-product of operations; it’s a strategic asset that can steer growth and innovation. To harness the true potential of data, it’s essential to first understand its role in the context of your business and work backwards from there. Our team has found that the concept can be illustrated as follows:
This may make the process look simple, but achieving this level of data and systems maturity is easier said than done. It requires fundamentally changing how your organization operates: from its culture and processes to leadership. It isn’t easy, but it’s not impossible, and one critical component to drive this transformation is a solid data foundation.
The Data Foundation working to your advantage
In their 2020 study, EY found that data is a strategic priority for all organizations with around 80% believing that improving data foundations would deliver significant value through increased productivity.
Essentially, a data foundation is the fundamental framework that supports good data management within an organization. How it is built for each organization depends on the role data plays in each business, but the fundamental elements and principles still stand.
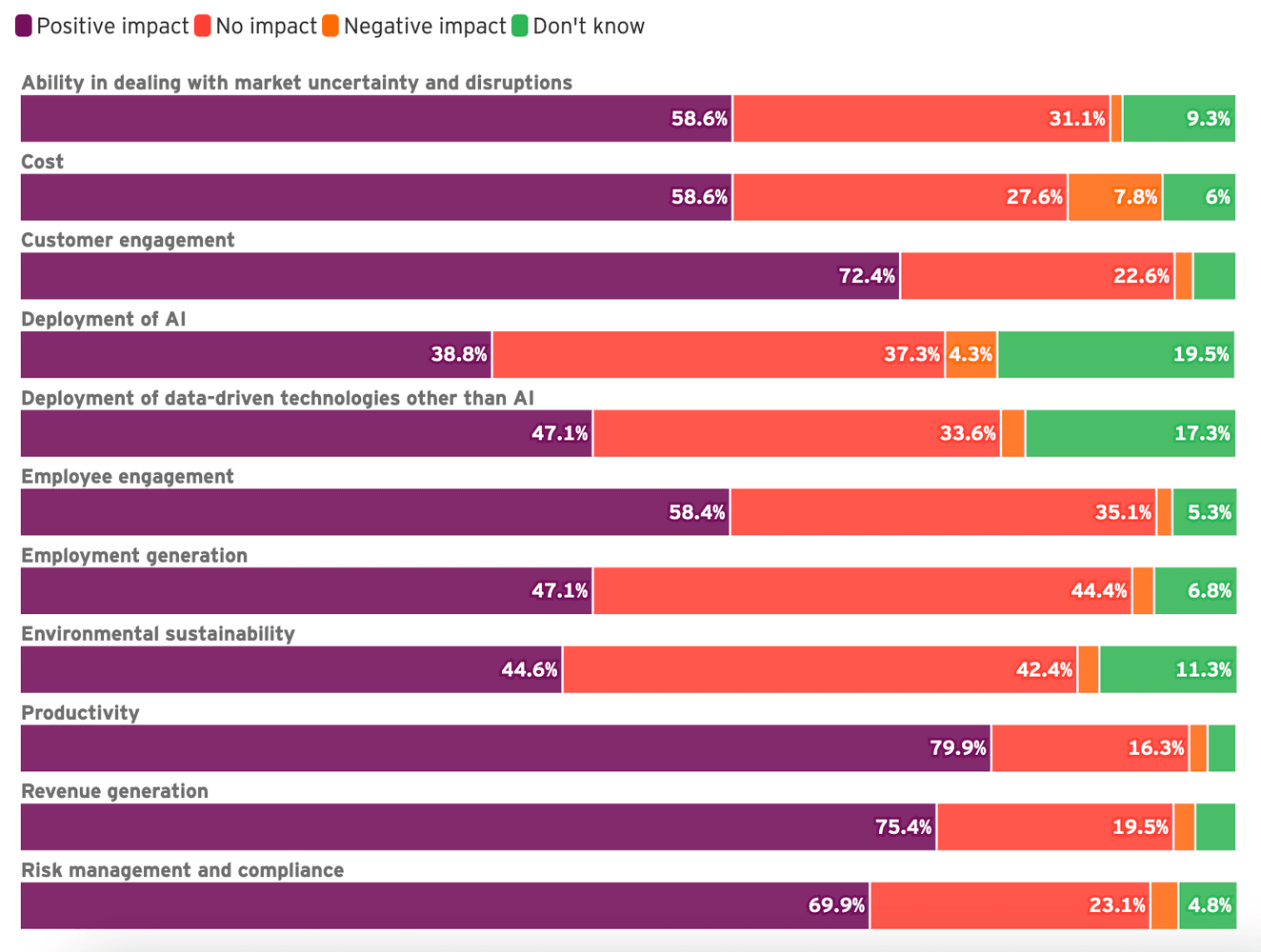
The following diagram illustrates how the EY survey respondents perceived the impact of a data foundation on businesses:
Key considerations for a strategic data foundation:
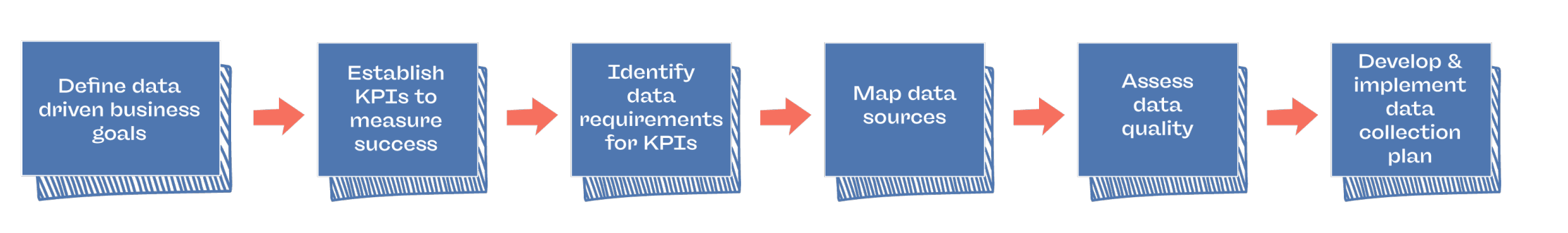
- Data collection: We start by identifying the data sources relevant to your business goals and systematically gather data from them.
- Data integration: ETL (Data extraction, transforming and loading) processes ensure consistency and accuracy in data extracted from multiple sources. In this process, relationships between data points from multiple sources are clearly defined.
- Data storage: Reliable solutions that organize data in a manner that makes it easy to access historical data, stream real-time data, conduct trend analyses, and develop long-term strategies.
- Data security and governance: Data security and governance policies ensure that data remains secure and compliant with regulations, while access controls mean it is only accessible by authorized personnel.
- Master Data Management (MDM): Focuses on maintaining a single, consistent, accurate version of key data entities across the organization. It ensures that core data is recorded in a consistent manner and serves as a reliable source of truth for applications and processes.
- Data architecture: This defines the overall structure of data within an organization through the design of databases, models, and data flow processes. These ensure that the data is organized, accessible, and aligns with the business’ goals and objectives.
What a good data foundation means for your organization
- A single source of truth: A solid data foundation means your organization has a centralized bank of accurate and consistent data, serving as the definitive source of truth for decision-making and analysis. This eliminates data silos and aids in the flow of information through your organization.
- First steps for a data-driven culture: By implementing data governance and promoting transparency, collaboration, and accountability, employees at all levels are empowered and equipped to make data-driven decisions.
- Significant economic gain: By eliminating data redundancies, automating tasks, and leveraging cloud infrastructure, you can lower an organization's data operational costs.
- Advanced analytics and reporting: Enabling advanced analytics by integrating data from various sectors in one place makes gathering insights for business decisions much easier.
- Automated workflows: Through proper integration, multiple applications can be connected to each other in order to respond to events belonging to business-critical workflows e.g., receiving a customer order may trigger other applications to update the inventory, generate invoices etc.
Challenges in building a Data Foundation
While building a data foundation is extremely promising for a company, the road to perfecting it and maintaining it is a continuous effort throughout an organization’s lifetime. Most of these issues stem from data quality/governance issues, integration complexities (usually driven by legacy systems), scalability and associated costs, and a data skills shortage.
How Villvay can help your organization
As mentioned before, there’s no cookie-cutter approach to building data foundations. Unlike selecting a CRM, which could involve choosing a single software solution, implementing a data foundation involves integrating multiple products and processes into one cohesive system.
At Villvay, we adhere to three guiding principles that shape our approach and ensure the success of your data foundation: Reusability, Agility, and Scalability.
Reusability: By creating reusable components and processes, we make it easier to adapt different parts of the foundation for use across various projects and departments. This means a level of consistency and standardization across the board but also saves precious time and resources as we are reusing modified existing elements. This way, instead of needing custom developments every time a business requirement changes, we need only tweak the existing components as necessary.
Agility: Being agile means we can adapt to feedback, challenges,, and new requirements as they arise. This iterative process involves continuous collaboration with stakeholders to refine and enhance the data foundation, ensuring it remains aligned with evolving business goals. This stands in contrast to the one-time implementation approach, which lacks flexibility and often results in a system that quickly becomes outdated.
Scalability: Our design process prioritizes handling increasing amounts of data and more complex requirements without compromising performance. This involves carefully selecting a combination of different technologies and designing an architecture model that supports horizontal and vertical scaling requirements unique to your business.
These principles are applied through all the phases of the process below:
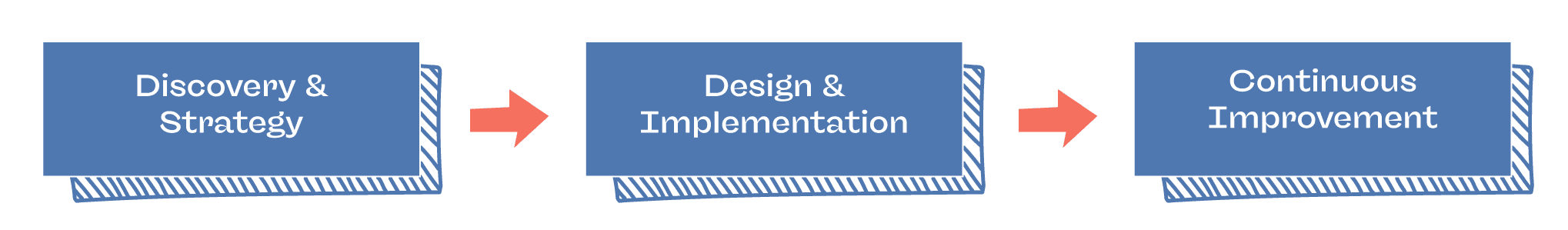
Discovery & Strategy
This initial phase focuses on understanding the business, its requirements, and the data landscape to define a strategic vision for data utilization. This is done by developing a strong data strategy, conducting thorough assessments and audits, and establishing effective data governance and compliance mechanisms.
Design and Implementation
Here, the data strategy is translated into actionable plans through the design and implementation of data architectures, governance frameworks, and management processes.
- Data architecture design and implementation
- MDM (Master Data Management)
- Data quality management
- Integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes
- Security and access control
- Scalability and performance optimization
Continuous improvement
In this phase, we focus on driving organizational adoption of the data-driven processes mentioned above and fostering continuous improvement to maximize data value—we know that as your business grows, so must your foundations.
